Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 02 junho 2024
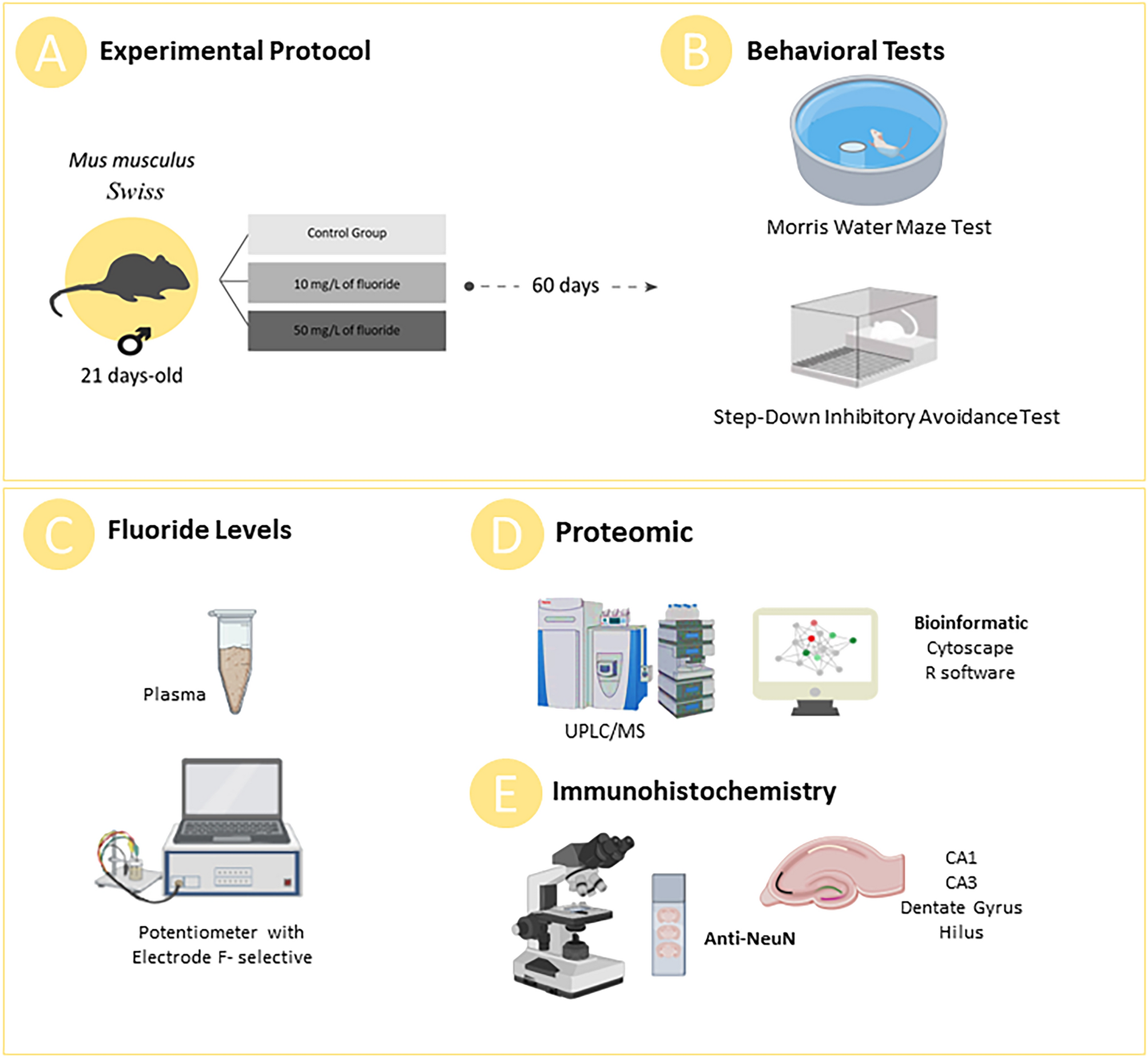

Long-term high fluoride exposure during adolescence causes hippocampal impairments

Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
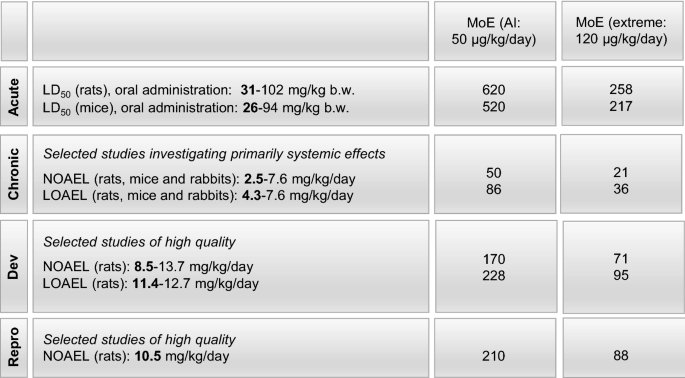
Toxicity of fluoride: critical evaluation of evidence for human developmental neurotoxicity in epidemiological studies, animal experiments and in vitro analyses
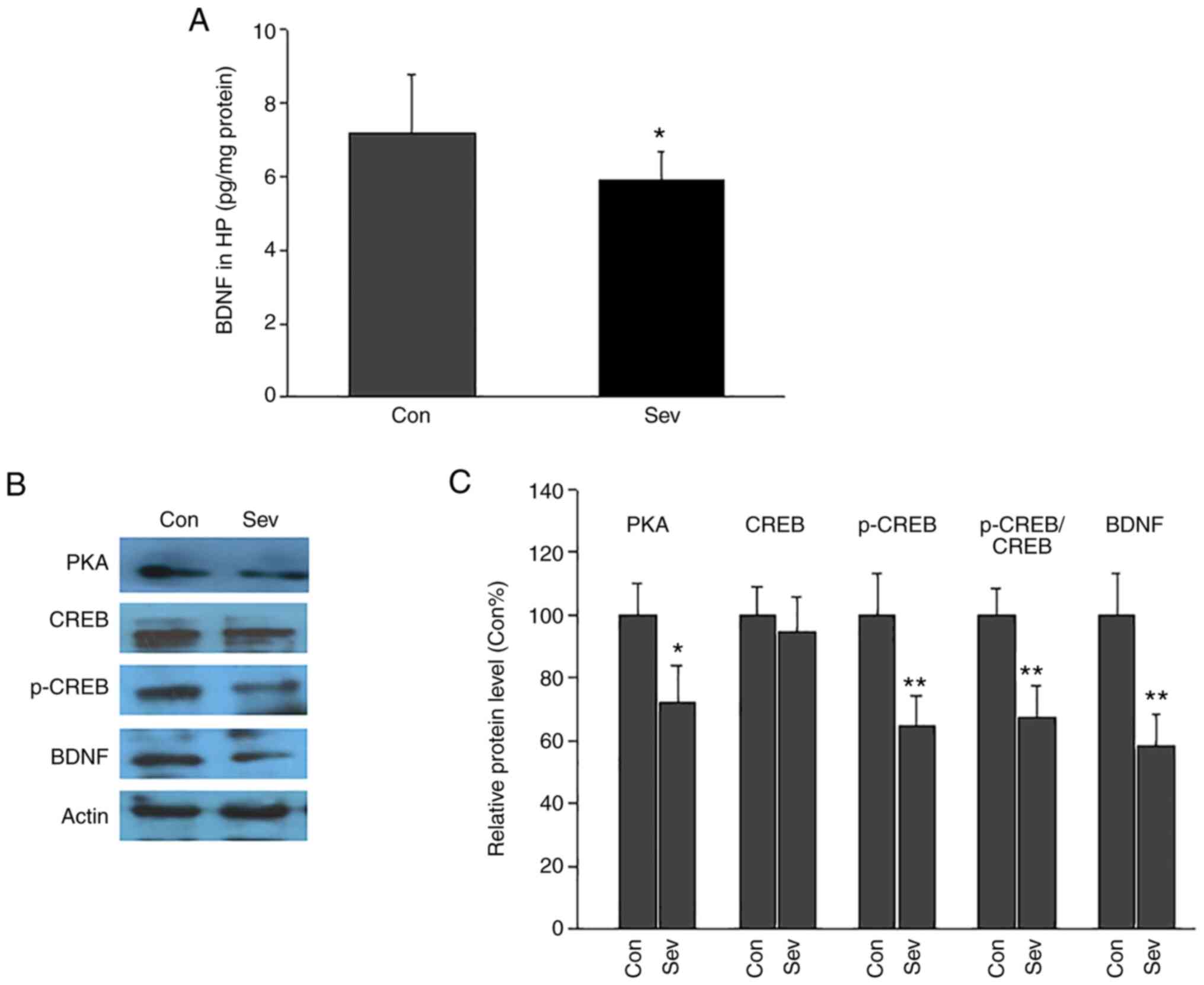
Repeated exposure to sevoflurane in neonatal rats impairs cognition in adulthood via the PKA‑CREB‑BDNF signaling pathway

Association between fluoride exposure in drinking water and cognitive deficits in children: A pilot study - ScienceDirect
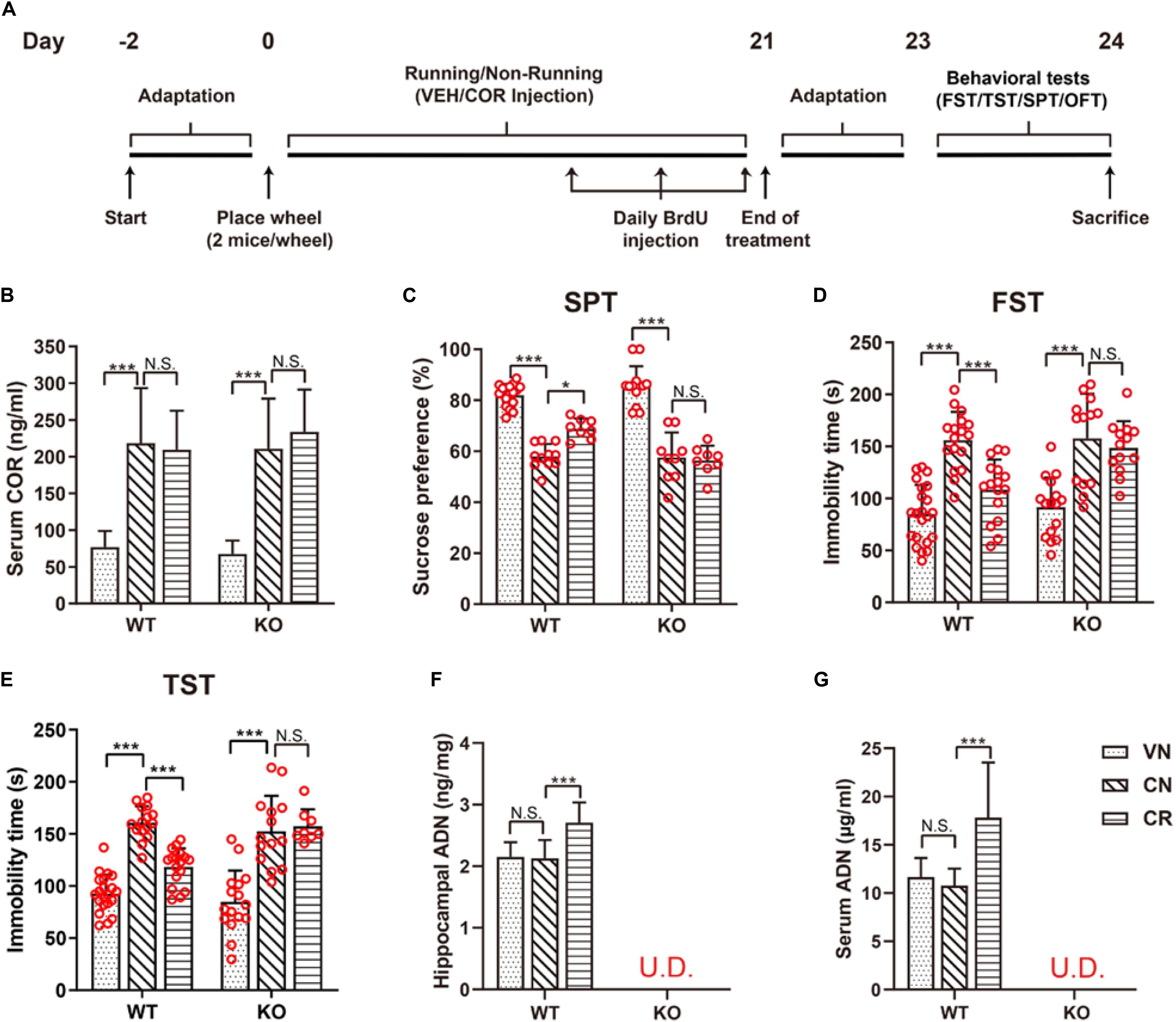
Frontiers Potential Involvement of Adiponectin Signaling in Regulating Physical Exercise-Elicited Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Dendritic Morphology in Stressed Mice

Dual Role of the P2X7 Receptor in Dendritic Outgrowth during Physiological and Pathological Brain Development

Early‐life stress affects the structural and functional plasticity of the medial prefrontal cortex in adolescent rats - Chocyk - 2013 - European Journal of Neuroscience - Wiley Online Library
Effects of long-term fluoride exposure are associated with oxidative biochemistry impairment and global proteomic modulation, but not genotoxicity, in parotid glands of mice

Chemical Aspects of Human and Environmental Overload with Fluorine
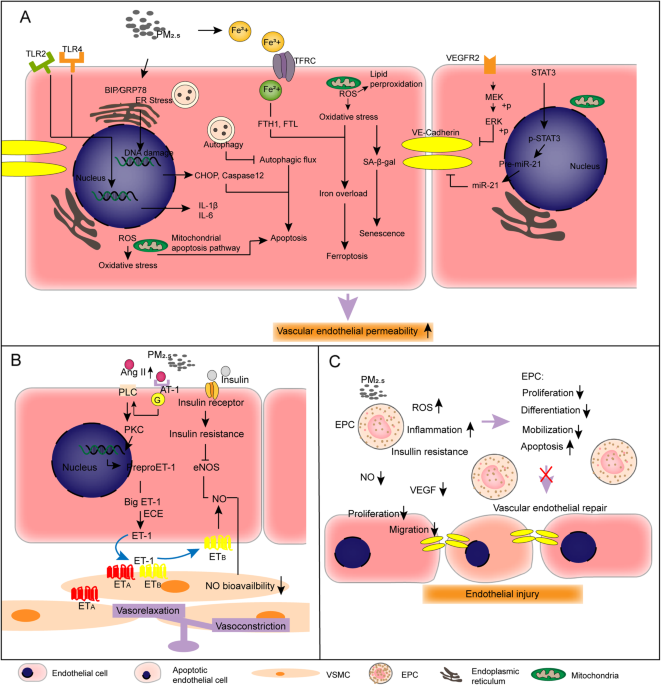
The critical role of endothelial function in fine particulate matter-induced atherosclerosis, Particle and Fibre Toxicology
Recomendado para você
-
 Brain Test Level 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100 Answers02 junho 2024
Brain Test Level 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100 Answers02 junho 2024 -
 Brain Test: Acertijos Engañosos Solución nivel 88 (español)02 junho 2024
Brain Test: Acertijos Engañosos Solución nivel 88 (español)02 junho 2024 -
 Brain test nivel 88 deja entrar al gato por favor se esta congelando02 junho 2024
Brain test nivel 88 deja entrar al gato por favor se esta congelando02 junho 2024 -
 nivel 88 brain test02 junho 2024
nivel 88 brain test02 junho 2024 -
brain test level 87|TikTok Search02 junho 2024
-
 how to beat level 82 on brain test day one|TikTok Search02 junho 2024
how to beat level 82 on brain test day one|TikTok Search02 junho 2024 -
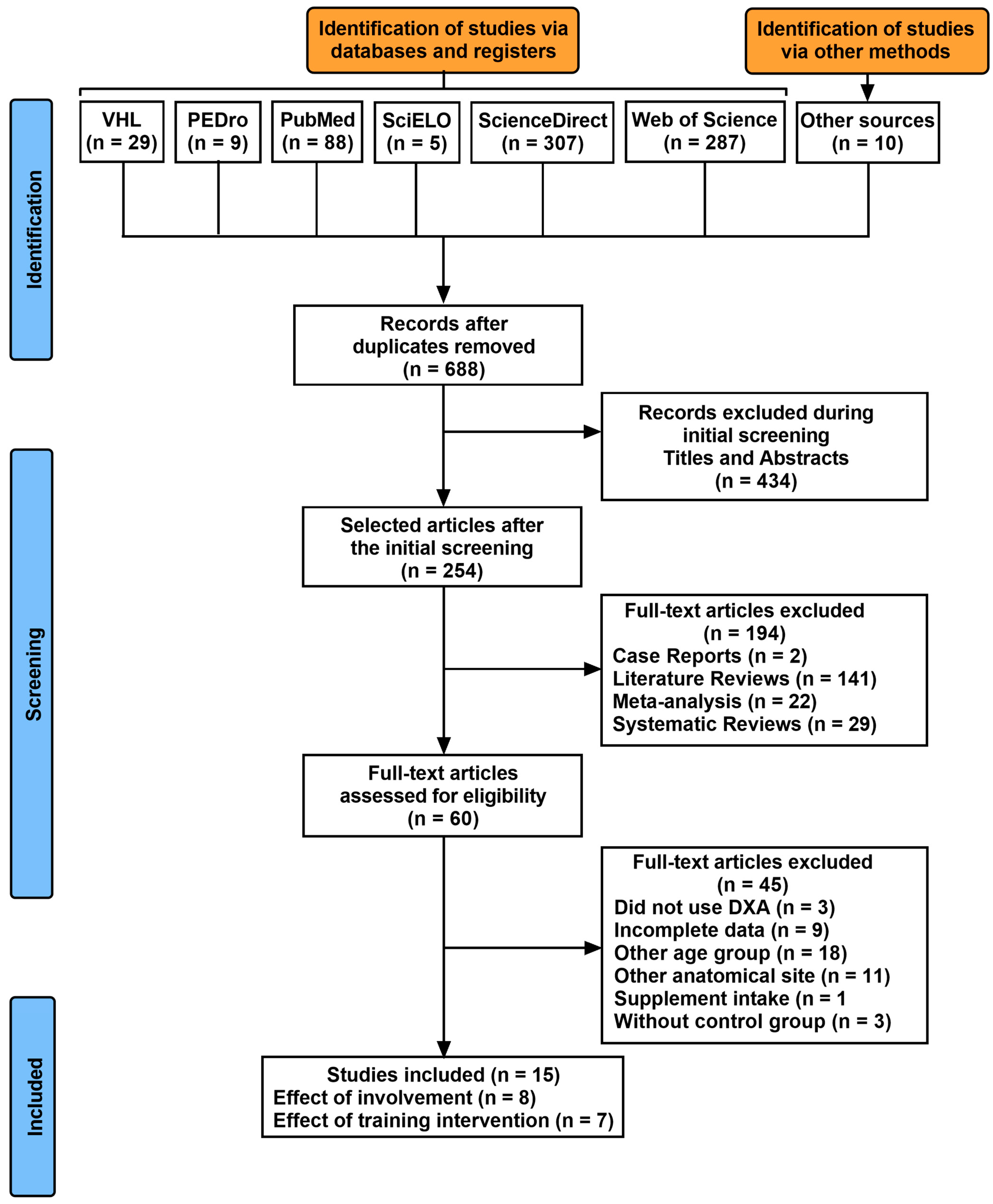 IJERPH, Free Full-Text02 junho 2024
IJERPH, Free Full-Text02 junho 2024 -
 Duskwood Dan draw - Desenho Dan Artistas, Desenho, Games de terror02 junho 2024
Duskwood Dan draw - Desenho Dan Artistas, Desenho, Games de terror02 junho 2024 -
 DEAR ZOO02 junho 2024
DEAR ZOO02 junho 2024 -
 Convite Animado Aniversário Ursinho Baloeiro - 1 Foto Mod 102 junho 2024
Convite Animado Aniversário Ursinho Baloeiro - 1 Foto Mod 102 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 All DRAGON BALL Videogames02 junho 2024
All DRAGON BALL Videogames02 junho 2024 -
 W. J. Thomas Mitchell American Academy of Arts and Sciences02 junho 2024
W. J. Thomas Mitchell American Academy of Arts and Sciences02 junho 2024 -
 Sonic Movie 3 (2024) - What To Expect In The Trilogy Conclusion02 junho 2024
Sonic Movie 3 (2024) - What To Expect In The Trilogy Conclusion02 junho 2024 -
 JUANMANUEL™ on X: Goku SSJ2 vs Majin Vegeta SSJ2. (Manga Full Color). / X02 junho 2024
JUANMANUEL™ on X: Goku SSJ2 vs Majin Vegeta SSJ2. (Manga Full Color). / X02 junho 2024 -
 Some partner RTX 4080 16GB cards costing more than entry-level RTX02 junho 2024
Some partner RTX 4080 16GB cards costing more than entry-level RTX02 junho 2024 -
 conjunto do adesivo elementos dentro Anos 2000 na moda estilo. interface. retro jogos interface, moderno estrutura para pc. nostálgico estilo. vetor ilustração. 24239622 Vetor no Vecteezy02 junho 2024
conjunto do adesivo elementos dentro Anos 2000 na moda estilo. interface. retro jogos interface, moderno estrutura para pc. nostálgico estilo. vetor ilustração. 24239622 Vetor no Vecteezy02 junho 2024 -
Kit Brinquedos De Maquiagem Para Crianças Menina Lavável Cosméticos Definir Jogo Fingir Princesa HYOY1201 - Escorrega o Preço02 junho 2024
-
Mikhail Tal vs Garry Kasparov 197802 junho 2024
-
 poki.monkey mart02 junho 2024
poki.monkey mart02 junho 2024 -
 turbo-ing the NSX?02 junho 2024
turbo-ing the NSX?02 junho 2024

