Labetalol infusion for refractory hypertension causing severe hypotension and bradycardia: an issue of patient safety, Patient Safety in Surgery
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 15 junho 2024
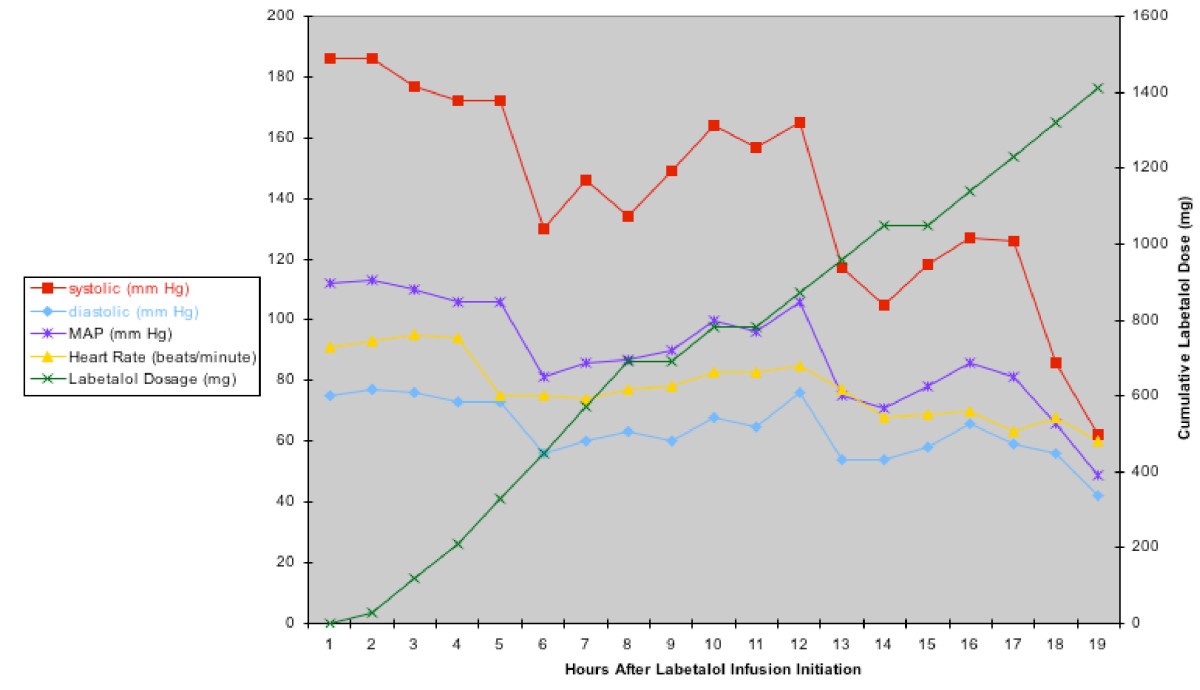
Incremental doses of intravenous labetalol are safe and effective and, at times, such therapy may need to be augmented by a continuous infusion of labetalol to control severe hypertension. Continuous infusions of labetalol may exceed the recommended maximum daily dose of 300 mg on occasion. We report a case in which hypertension occurring after an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, initially responsive to intermittent intravenous beta-blockade, became resistant to this therapy leading to the choice of an intravenous labetalol infusion as the therapeutic option. The labetalol infusion resulted in a profound cardiovascular compromise in this postoperative critically ill patient. While infusions of labetalol have successfully been used, prolonged administration in the intensive care unit requires vigilance and the establishment of a therapeutic rationale/policy for interventions, such as the ready availability of glucagon, β-agonists, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, insulin, and vasopressin when severe cardiovascular depression occurs.

PDF) Safety and efficacy of continuous intravenous labetalol for blood pressure control in neurosurgical patients
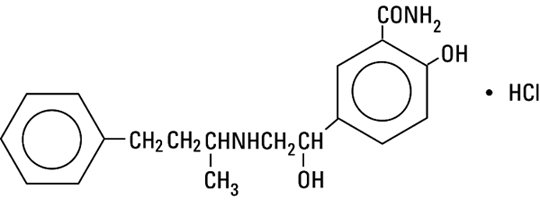
Labetalol: Package Insert
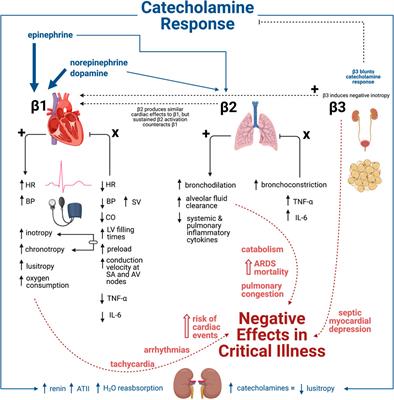
Frontiers Beta-Adrenergic Blockade in Critical Illness

Hemodynamic Safety of Continuous Infusion Labetalol Versus Esmolol Combination Therapies for Type B Aortic Dissections

Management of Women With Acquired Cardiovascular Disease From Pre-Conception Through Pregnancy and Postpartum: JACC Focus Seminar 3/5 - ScienceDirect

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE injection

Use of Medication for Cardiovascular Disease During Pregnancy: JACC State-of-the-Art Review

Carvedilol Among Patients With Heart Failure With a Cocaine-Use Disorder
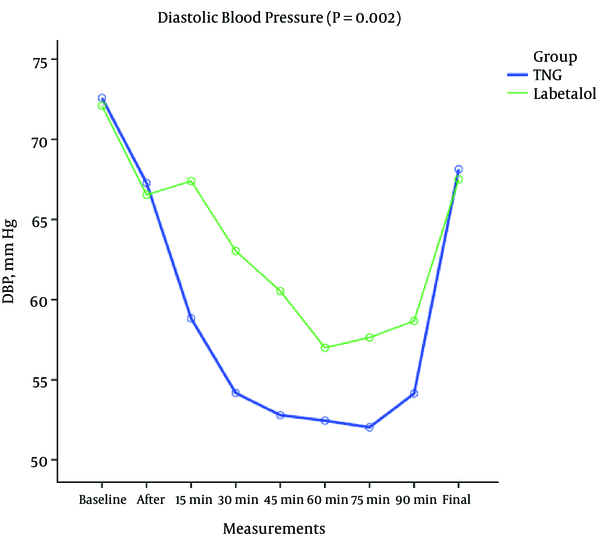
Comparing Labetalol and Nitroglycerine on Inducing Controlled Hypotension and Intraoperative Blood Loss in Rhinoplasty: A Single-Blinded Clinical Trial, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine

PDF] Managing Hypertension in Patients With Stroke Are You Prepared for Labetalol Infusion

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated

Full article: Remifentanil versus labetalol for deliberate hypotensive anesthesia in children undergoing cochlear implantation: A randomized clinical trial
Recomendado para você
-
Labetalol (Normodyne) Vial, 5mg/mL15 junho 2024
-
 LABETALOL HCl (HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst): FDA Package Insert15 junho 2024
LABETALOL HCl (HF Acquisition Co LLC, DBA HealthFirst): FDA Package Insert15 junho 2024 -
 LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP15 junho 2024
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP15 junho 2024 -
 LABETALOL INJ 5MG/ML - RX Products15 junho 2024
LABETALOL INJ 5MG/ML - RX Products15 junho 2024 -
 Alvogen 5mg/mL Labetalol HCl in 40mL Mutiple Dose Vial - Predictable Surgical Technologies15 junho 2024
Alvogen 5mg/mL Labetalol HCl in 40mL Mutiple Dose Vial - Predictable Surgical Technologies15 junho 2024 -
 Labebet 100 MG Tablet (10): Uses, Side Effects, Price & Dosage15 junho 2024
Labebet 100 MG Tablet (10): Uses, Side Effects, Price & Dosage15 junho 2024 -
Labebet 100 MG Tablet - Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Price, Composition15 junho 2024
-
 LABETALOL HCL 100MG/20ML MDV 20ML - HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS USA INC15 junho 2024
LABETALOL HCL 100MG/20ML MDV 20ML - HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS USA INC15 junho 2024 -
 Oral antihypertensive regimens (nifedipine retard, labetalol, and methyldopa) for management of severe hypertension in pregnancy: an open-label, randomised controlled trial - The Lancet15 junho 2024
Oral antihypertensive regimens (nifedipine retard, labetalol, and methyldopa) for management of severe hypertension in pregnancy: an open-label, randomised controlled trial - The Lancet15 junho 2024 -
 Hypertension during the Acute Phase of Stroke15 junho 2024
Hypertension during the Acute Phase of Stroke15 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 New Subway Surfers Collectible 2 Mini Figures Skating Jake With Lit Sticker15 junho 2024
New Subway Surfers Collectible 2 Mini Figures Skating Jake With Lit Sticker15 junho 2024 -
 Etihw in black Grey gardens, Gray gardens, Shadow king15 junho 2024
Etihw in black Grey gardens, Gray gardens, Shadow king15 junho 2024 -
 emoji faces expression funny smile happy angry mood sad set15 junho 2024
emoji faces expression funny smile happy angry mood sad set15 junho 2024 -
 Jogos de futebol hoje, quarta, 21 de abril; onde assistir e horários15 junho 2024
Jogos de futebol hoje, quarta, 21 de abril; onde assistir e horários15 junho 2024 -
 LOUD 🇧🇷 on X: Ja tá rolando alguns anuncios no marketplace do LOUD CLUB Anunciaram a Jaqueta LOUD Influencers por R$1848,90 e tem mousepad por R$49,30 IRMAO / X15 junho 2024
LOUD 🇧🇷 on X: Ja tá rolando alguns anuncios no marketplace do LOUD CLUB Anunciaram a Jaqueta LOUD Influencers por R$1848,90 e tem mousepad por R$49,30 IRMAO / X15 junho 2024 -
 Chesskid.com Pin15 junho 2024
Chesskid.com Pin15 junho 2024 -
Harry Potter & The Desi Memes (@maglumemes) • Instagram photos and15 junho 2024
-
 Pra vocês esse também é o melhor anime de esporte de todos os tempos? : r/animebrasil15 junho 2024
Pra vocês esse também é o melhor anime de esporte de todos os tempos? : r/animebrasil15 junho 2024 -
Giving Away Free Project Slayers code everday #projectslayers #private15 junho 2024
-
 Crunchyroll Adds Lostorage conflated WIXOSS, My Sweet Tyrant15 junho 2024
Crunchyroll Adds Lostorage conflated WIXOSS, My Sweet Tyrant15 junho 2024