Effect of perioperative magnesium sulfate and labetalol infusion on peripheral perfusion and postoperative pain in nasal surgery: a randomized controlled trial, Patient Safety in Surgery
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 02 junho 2024
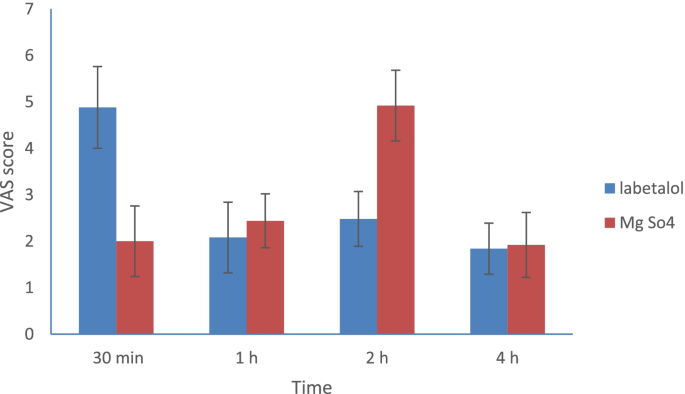
Maintenance of adequate peripheral perfusion during controlled hypotension is necessary for patient safety and improved surgical outcomes during controlled hypotension in nasal surgery. The hypothesis of this study was to investigate the effect of perioperative magnesium sulfate and labetalol infusion on peripheral perfusion and postoperative pain in patients undergoing nasal surgery. A total of 50 patients were randomly assigned into two equal groups in this double-blind clinical study: the magnesium sulfate group; received 40 mg/kg loading dose of intravenous (IV) magnesium sulfate followed by 10–15 mg/kg/h continuous IV infusion and the labetalol group; received 0.25 mg/kg loading dose of IV labetalol followed by 0.5–1 mg/kg/h continuous IV infusion to achieve a mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) of = 55–65 mmHg. The primary outcome was to compare the effect of perioperative magnesium sulfate and labetalol infusion on peripheral perfusion during nasal surgery. The secondary outcomes were the assessment of serum lactate, postoperative pain, time to the first call for pethidine (rescue analgesic) and total pethidine consumption. PPI was comparable between the groups at baseline, intubation, and 5 min. In contrast, magnesium sulfate group had a significantly higher PPI than the labetalol group. The magnesium sulfate group had a significantly higher MABP and heart rate compared to labetalol group. The time to reach the target MABP was significantly prolonged in magnesium sulfate than the labetalol group [21.6 ± 1.7 vs 6.9 ± 1.5] min. VAS scores were significantly lower for 2 hs postoperatively in the magnesium sulfate group than the labetalol group. The time to first call of pethidine was significantly prolonged in the magnesium sulfate group compared to the labetalol group [113.1 ± 5.2 vs 28.2 ± 1.5] min. Magnesium sulfate maintains wider PPI and offers better postoperative pain relief compared to labetalol during induced hypotension in nasal surgery. Institutional review board approval (ref: 6601/20–12-2020). Clinicaltrial.gov (ref: NCT04688203 , date of registration: 29 -12–2020).

Controlled hypotension for FESS: A randomised double-blinded

View of A randomized controlled trial of dexmedetomidine vs
The Effects of Hypocapnia and Hypercapnia on Intraoperative

2023 Australasian Anaesthesia – Blue Book by anzca1992 - Issuu

Anaesthesia for laparoscopic surgeries

2009 ACCF/AHA Focused Update on Perioperative Beta Blockade
Obstetric Regional Anesthesia - NYSORA

Effects of esmolol continuous infusion on blood loss in patients

Effects of esmolol continuous infusion on blood loss in patients

Management of Patients after Vascular Surgery - ppt download
Physiological Changes in the Pregnancy and Anesthetic Implication

PDF) Comparing remifentanil, magnesium sulfate, and

Abstracts - 2023 - Anaesthesia - Wiley Online Library

Guidelines for the Early Management of Adults With Ischemic Stroke

Calaméo - Absolute Neurocritical Care Review 2017
Recomendado para você
-
Labetalol: Uses, Side Effects, Dosage & Reviews02 junho 2024
-
 Betalor 5/25mg com 30 cápsulas - Ache02 junho 2024
Betalor 5/25mg com 30 cápsulas - Ache02 junho 2024 -
 Fosun Pharma USA Inc 72266010301 - McKesson Medical-Surgical02 junho 2024
Fosun Pharma USA Inc 72266010301 - McKesson Medical-Surgical02 junho 2024 -
 Almaject Inc 47781058629 - McKesson Medical-Surgical02 junho 2024
Almaject Inc 47781058629 - McKesson Medical-Surgical02 junho 2024 -
 Labetalol (hydrochloride) (AH 5158A, Normodyne, NSC 290312, SCH 15719W, Trandate, CAS Number: 32780-64-6)02 junho 2024
Labetalol (hydrochloride) (AH 5158A, Normodyne, NSC 290312, SCH 15719W, Trandate, CAS Number: 32780-64-6)02 junho 2024 -
 Labetalol Tablet Wholesalers & Supplier - Oddway International®02 junho 2024
Labetalol Tablet Wholesalers & Supplier - Oddway International®02 junho 2024 -
 Labetalol02 junho 2024
Labetalol02 junho 2024 -
 Labetalol Tablet IP02 junho 2024
Labetalol Tablet IP02 junho 2024 -
 Labetalol Tablets General Medicines at Best Price in Mumbai02 junho 2024
Labetalol Tablets General Medicines at Best Price in Mumbai02 junho 2024 -
 Figure 2 from The low/high BCS permeability class boundary: physicochemical comparison of metoprolol and labetalol.02 junho 2024
Figure 2 from The low/high BCS permeability class boundary: physicochemical comparison of metoprolol and labetalol.02 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Wikipedia Wikiwand Wikimedia project World map, world, map png02 junho 2024
Wikipedia Wikiwand Wikimedia project World map, world, map png02 junho 2024 -
 Piece Teorias: janeiro 201602 junho 2024
Piece Teorias: janeiro 201602 junho 2024 -
Roblox studio, LogoWiki Wiki02 junho 2024
-
 Dragon Ball GT (Dublado)02 junho 2024
Dragon Ball GT (Dublado)02 junho 2024 -
 120 Best Funny anime pfp ideas anime, anime funny, funny anime pics02 junho 2024
120 Best Funny anime pfp ideas anime, anime funny, funny anime pics02 junho 2024 -
 BAHIA TEM INTERESSE NA CONTRATAÇÃO DE WESLEY02 junho 2024
BAHIA TEM INTERESSE NA CONTRATAÇÃO DE WESLEY02 junho 2024 -
 jogos para jogar no Google02 junho 2024
jogos para jogar no Google02 junho 2024 -
 Plasma Wings Roblox Microsoft Exclusive. Virtual Item Code Only Through Messages02 junho 2024
Plasma Wings Roblox Microsoft Exclusive. Virtual Item Code Only Through Messages02 junho 2024 -
 Finally! A Protective Case for ROG Ally Hand-Held With A Kickstand02 junho 2024
Finally! A Protective Case for ROG Ally Hand-Held With A Kickstand02 junho 2024 -
 playing papa's burgeria to go for the first time02 junho 2024
playing papa's burgeria to go for the first time02 junho 2024
